33 Safety Checks
Michael Hrycay
Learning Objectives
List common safety checks.
Introduction
Warehouse work involves a wide range of tasks and hence a wide range of health and safety hazards. Here are some of the injuries and illnesses that can occur:
- cuts and amputations from the use of knives, cutters, saws, packaging tools and materials
- burns from contact with live electrical conductors or hot equipment engines
- crushing injuries from material handling equipment and processes.
- electric shock or electrocution from power tools, defective switch panels, accidental contact with electric power lines, or cleaning of equipment that hasn’t been turned off
- slips and falls from slippery or cluttered floors or inadequate lighting
- soreness and loss of function of wrists and arms due to repeated awkward movements or vibration, or working in one position for a long time
- back pain from lifting heavy or awkward loads and using awkward postures
- itching, swelling, redness of skin from temperature extremes, physical abrasion, exposure to detergents or cleaning solutions
- allergies and skin disorders from contact with metals and contaminated packages, inhalation of dusts and plant materials
- illness due to exposure to chemicals and pesticides, or contact with packages contaminated with biological infectious materials such as animal droppings
- carbon monoxide poisoning from internal combustion engine emissions due to poor vehicle maintenance and inadequate ventilation
- battery charging hazards from electric powered forklifts and other battery powered equipment
To minimize the risk of these hazards, it is important to know what safety features are available on equipment and check equipment at each use.
Common Hazards and Safety Checks
There are harzards specific to your work environment that your employer must make you aware of. However, the following are some general hazards and safety checks you can perform under any circumstances.
In the Warehouse and Terminal
Floors
| Risk | Safety Check |
| Slips and falls | Provide ample space for work and loads |
| Hit by falling objects | Check for obstructions, debris, lubricants and moisture |
Ramps
| Risk | Safety Check |
| Slips and falls | Make sure handrails are installed. |
| Hit by rolling carts and trolleys | Check nonskid surfaces aren’t peeling off or causing a tripping hazard. |
Aisles
| Risk | Safety Check |
| Slips and falls | Be aware of doors that open into aisles |
| Collisions | Identify if there is adequate lighting. Observe mirrors at blind corners to avoid collisions. |
Ladders
| Risk | Safety Check |
| Falls | Missing, cracked, twisted, distorted, split, or worn rails |
| Loose step rungs, rust, oxidization, excessive wear including smoothed out nonslip surfaces | |
| Locks that are not latching properly when ladder is extended | |
| Missing identification label. All ladders must have the CSA identification label. | |
| Any alterations: all safety equipment must not be modified or altered in any way. |
Loading Docks
| Risk | Safety Check |
| Slips, falls, cuts | Check for obstructions, debris, spills, snow, and stored items |
| Being crushed between a truck and loading dock | All rolling material and equipment should be choked or have wheels locked. |
| Being caught between 2 vehicles | Be aware of vehicles and stay far enough away so as to be visible by the driver. |
| Being hit by falling materials or equipment | |
| Being caught by conveyors | |
| Being hit by moving equipment |
Vehicles
| Risk | Safety Check |
| Being caught under a vehicle | Check that an engine cannot be started while loading and unloading the vehicle. |
| Amputations | Check that rolling equipment is choked or has wheels locked. |
| Being caught between a vehicle and dock boards |
Materials Handling
Shipping and Packing
Risks in shipping and packing include:
- finger or hand injuries
- back injuries
- leg and foot injuries
- exposure to toxic chemicals
- eye injury if the strapping breaks and snaps in the eyes
To mitigate the above risks:
- Check the condition of PPE when using sealers and glue. Chemicals have toxic vapour and may cause skin irritation.
- Check for exposed sharp edges when using strapping. Trim any sharp pointed edges with metal snips or cutters.
- Ensure exhaust is working when using hot shrink wrap machines, bag sealers, and plastic strapping welders.
- Check guard rails and mirrors are in place on mechanized picking equipment.
Materials and Handling Equipment
Common risks associated with materials handling equipment include:
- slips, trips and falls
- crushed hands
- collisions
To mitigate the above risks, perform the following checks:
Carts
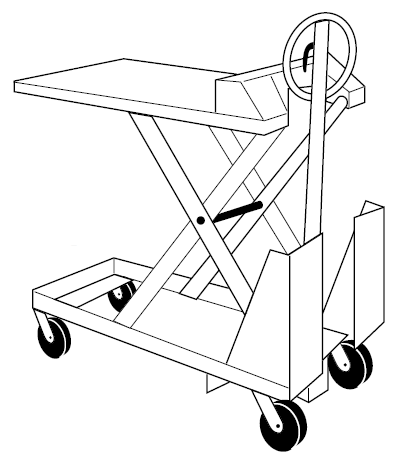
- A lift cart shouls have hand guards- make sure they are installed
- Check to make sure wheels are not loose and unstable. Make sure any wheel locking mechanism is operational.
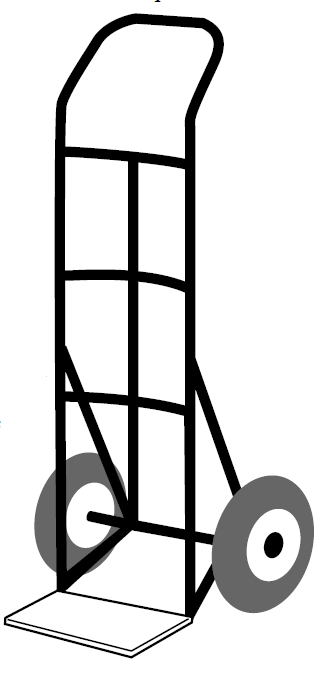
- ensure straps are available and in good conditions for over size loads
- ensure wheels are tight on the axle and not wobbly
- some handles are extendable. Make sure any clips holding the handle in place are installed and secure.
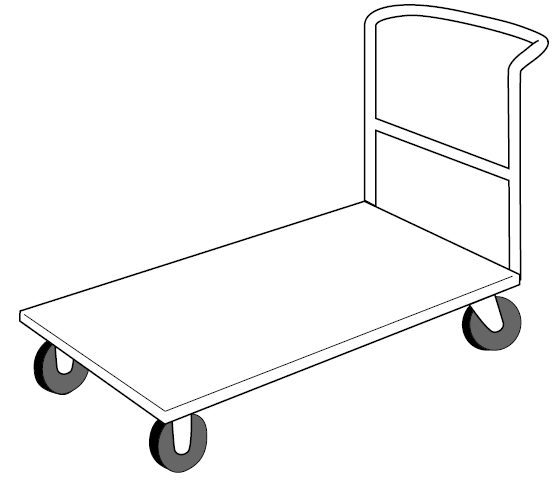
- Ensure that handles are at protected places on the racks or body of the cart so that traffic, walls, or other objects being passed will not crush or scrape your hands.
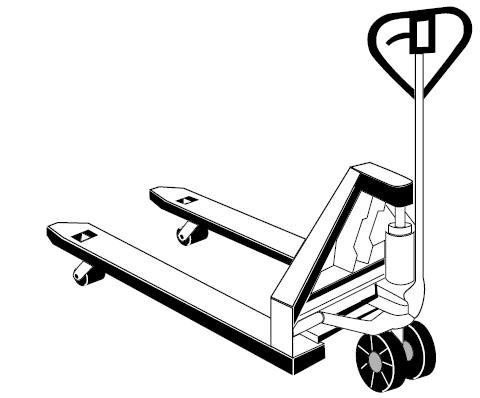
- Check to make sure the lift mechanism is adjusted properly so the forks remain level as they lift.
- Check to make sure the fork wheels are in alignment.
Conveyors
- Ensure the area is properly lit
- Do not wear loose clothing, jewellery. Ensure long hair is tied.
- Ensure any guard rails along sides and pinch points between the conveyor system and fixed objects are in place and secure.
Rollers and Dollies
- Check to make sure chocks are available for use when loading or unloading.
Hand Held Power Tools
Some hazards are particular to power tools, specifically related to electricity:
- electrical shosk
- burns
- noise
To mitigate these hazards:
- Ensure all cords are free from cracks and freys.
- Ensure blades and bits are sharp. Dull blades and bits can produce exessive noise or heat.
- Make sure the guards on saws are installed.
- Make sure any electrical outlets or extension cords have the ground lead in place.
Hand Held Manual Tools
- Ensure the quality of the chisel suits the purpose. Consumer grade tools are not designed for heavy or continuous use
- Ensure the blade is sharp and free from burs or nicks.
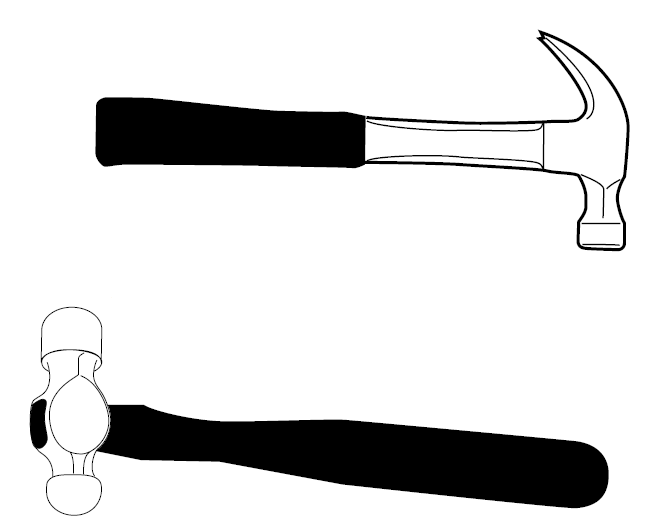
- Ensure the head is tight on the handle. Do not use a hammer with a loose head.
- Ensure the handle is not cracked or damaged.
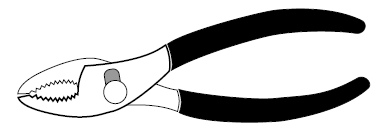
- Ensure pliers are lubricated and clean
- Ensure the jaws are not bent or nicked
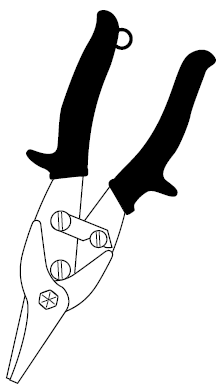
- Check to see if jaws are tight and lubricated
- Check to see you are using the correct snip. There are different snips for left and right hand cuts.
- Ensure you are cutting flat material with snips, not round material like wires or cables
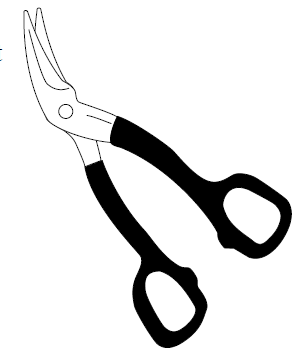
- Similar to snips, jaws must be tight and lubricated. Do not use cutters where there is a gap inbetween the jaws.
Powered Vehicles for Moving and Lifting
Only used powered vehicles if you are properly trained and certified.
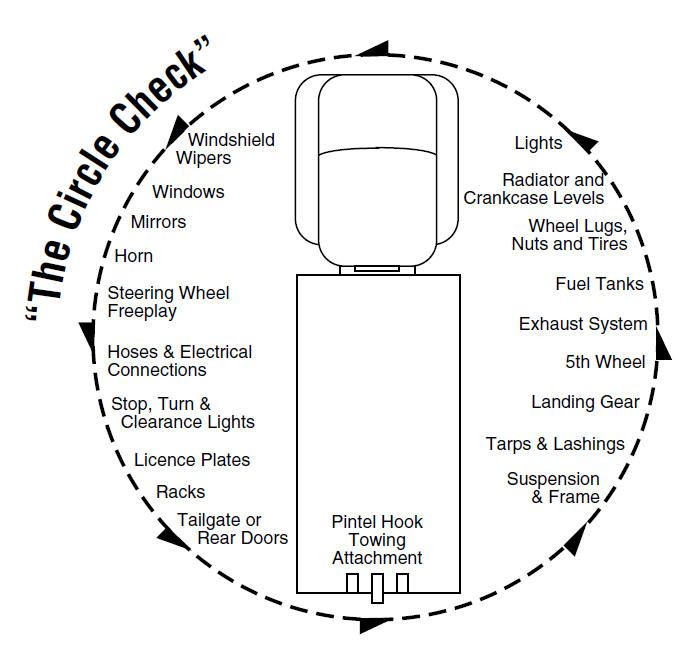
At the start of the shift your employer may have a checklist for you. Go through the checklist and mark the condition of all items. The following diagram describes “the circle check.”
References
Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. (2011). Warehouse Workers Safety Guide.

