19 Common Work Area Hazards
Michael Hrycay
Learning Objectives
Appraise work area for hazards
Cuts
Cuts can involve:
- knives
- furniture
- equipment
- counters
- utensils
- preparation areas
- glassware and cans
- food wrap container blades
- cleaning equipment
- dishes
To prevent cuts:
- Use a proper cutting board and slip-resistant matting to prevent the board from sliding on the counter.
- Store knives in a knife rack or drawer, with the handles facing the front.
- Keep your knife at the back of the counter with the blade facing away from you when it is not in use.
- Keep knives sharpened.
- Discard broken or chipped glassware and opened cans carefully.
- Wear appropriate PPE(personal protective equipment)
- Do not try to catch anything as it falls – wait until it stops moving before you pick it up.
Safe Use of Power Equipment
- Get proper training in operating the equipment and doing the job safely before using any equipment
- Follow the manufacturer’s instruction manual when you operate, clean and maintain the equipment.
- Ensure that proper lock out/tag out procedures are in place (e.g., unplug any broken or unsafe equipment, attach a warning tag, take it out of use and tell your supervisor).
- Keep your hands out of feed hoppers and delivery chutes – use a food pusher to load the machine.
- Use a knife to finish the cutting when something becomes too thin for the slicer.
- Put all guards and safety devices back in place after cleaning.
- Cover your hair, tuck in loose or frayed clothing and remove your gloves and jewelry. All of these can get caught in equipment with moving parts.
- DO NOT operate the equipment if you feel drowsy or unwell. Remember, some cold remedies can make you feel sleepy.
To work safely with machines that have blades:
- Make sure cutting blades are sharp.
- Keep your hands away from the edges of cutting blades – make sure you can see both your hands (and all your fingers) as well as the cutting blades.
- Keep your hands away from all moving parts and avoid cleaning or brushing off moving parts such as cutting blades or beaters in mixers.
- Ensure that proper guards are in place and correctly adjusted.
Burns and Scalds
Burns and scalds can occur when you use:
- stoves
- toasters, ovens and toaster ovens
- deep fryers
- hot utensils
- pressure cookers
- coffee makers
- steamers
- cooking pots, and
- hot dishwashers.
To prevent burns and scalds:
- Be aware that deep fat fryers are the number one cause of burns.
- Open hot water and hot liquid taps slowly to avoid splashes.
- Follow all electrical and fire safety guidelines.
- Follow the manufacturer’s operating instructions for all equipment.
- Use only recommended temperature settings for each type of cooking.
- Use proper PPE.
To use stoves and ovens safely:
- Turn off the electric elements and gas flames of stoves when they are not in use.
- Wear oven mitts to handle hot objects – use long gloves for deep ovens.
- Release the pressure safely before you open cookers and steam ovens and face away from opening doors.
- Use the right size burner for the size of the pot or pan.
- Report any defects, problems or faults to your supervisor.
When handling pots and pans:
- WEAR long-sleeved cotton shirts and cotton pants.
- ORGANIZE your work area to prevent contact with hot objects and flames.
- LET people know when you are carrying a hot item. MAKE sure pots and pans are not overfilled.
- REMOVE metal spoons from pots and pans while cooking.
- AVOID letting hot water contact hot oil.
- MOVE closer or use a tool when you have to reach for something, rather than overstretching.
- STAND to the side when you work with pots containing boiling liquids.
- USE proper PPE.
Take special care when handling pot handles and lids:
- KEEP pot handles away from hot burners and make sure they don’t stick out from the counter or cooking stove.
- OPEN lids by lifting the far edge first.
- USE oven mitts or a dry cloth to lift lids from hot pots – wet cloths conduct heat and can scald you.
- ASSUME that all pots, pans and metal handles are hot – touch them only when you are sure they are safe, or when you are wearing proper gloves.
Slips and Falls
Slips and falls can result from:
- slippery and cluttered floors and stairs
- loose or bumpy carpets and floor mats
- defective ladders and footstools
- poor visibility, and
- wet and greasy areas.
To prevent slips and falls:
- MAKE sure that wooden duckboards and railings are in good repair and free of splinters.
- CHECK that ladders and footstools are in good repair and have non-skid feet.
- TAKE defective ladders or footstools out of use until they are repaired or replaced.
- REPLACE burnt-out light bulbs and fluorescent tubes as soon as possible.
- ENSURE that outside areas used to receive deliveries or take out garbage are well lit and free of obstructions.
- USE ladders, for climbing, rather than unsafe substitutes such as chairs, stools or boxes.
- CLOSE oven, dishwasher and cupboard doors when you’re not using them – open doors may trip you or your co-workers.
To prevent floor hazards:
- REPORT any tripping or slipping hazard to your supervisor right away.
- KEEP floors and stairs clean, dry and non-slippery. CLEAR debris and obstructions from floors and stairs.
- USE slip-resistant waxes to polish and treat floors. WEAR proper shoes with slip-resistant soles.
- MAKE sure that carpeting, rugs and mats are free of holes, loose threads, loose edges and bumps that may cause tripping.
- USE warning signs for wet floors and other hazards.
Exposure to Hazardous Products
Exposure to hazardous products can occur from:
- cleaners (e.g., sink, oven, floor, stainless steel),
- bleaches,
- dishwasher soap,
- degreasers, and
- descalers.
To prevent exposure to hazardous products:
- ASK your supervisor about possible harmful effects of the products you use.
- MAKE sure you receive WHMIS training in the safe use, handling, storage and disposal of products. WHMIS stands for Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System.
- READ the label on the container.
- FOLLOW the manufacturer’s instructions for use.
- USE only products that are stored in clearly labelled containers.
- WORK in a well-ventilated area. USE proper PPE.
- KNOW where to find the material safety data sheets/ safety data sheets (MSDSs/SDSs) for the products you use – These sheets give you important information about hazards, safe use and first aid.
- GET proper first aid and medical help if you breathe in, swallow or come into contact with a toxic product.
To store hazardous products safely:
- KEEP them in suitable containers and label clearly – not in food containers.
- LOCK up hazardous product containers in a designated storage area marked with warning signs.
- PLACE hazardous products on lower shelves, below eye level, rather than on top shelves.
- STORE protective equipment separately from hazardous products.
To handle hazardous products safely:
- WEAR the personal protective equipment required by your employer.
- USE separate spoons, scoops or cups rather than cooking utensils, food containers or your hands to dispense hazardous products.
- USE a utensil made from a material that won’t react with the hazardous product to dispense liquids and powders instead of using plastic spoons.
- CLOSE hazardous product containers after use.
Electrical Safety
Hazards
Common electrical hazards are electric shock and electro- cution. These can occur from contact with:
- faulty electrical tools and equipment,
- faulty appliances and wires,
- electrical outlets,
- switch panels, and
- electric transformers.
Prevention
- INSPECT equipment, power cords, and electrical fittings for damage prior to each use. Repair or replace damaged equipment.
- SWITCH equipment OFF before connecting them to a power supply and before making adjustments.
- ENSURE that electrical equipment is properly grounded or double-insulated. The grounded equipment must have an approved 3-wire cord with a 3-prong plug. This plug should be plugged in a properly grounded 3-pole outlet.
- TEST all electrical equipment for effective grounding with a continuity tester or a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) before use.
- KEEP power cords clear of the equipment during use.
- SUSPEND power cords over aisles or work areas to eliminate stumbling or tripping hazards.
- COVER open electrical outlets with plastic safety plugs CHECK power cords and plugs daily. Discard if worn or damaged. Any cord that feels more than comfortably warm should be removed from use, replaced, or checked by an electrician.
- ELIMINATE octopus connections.
- PULL THE PLUG, NOT THE CORD.
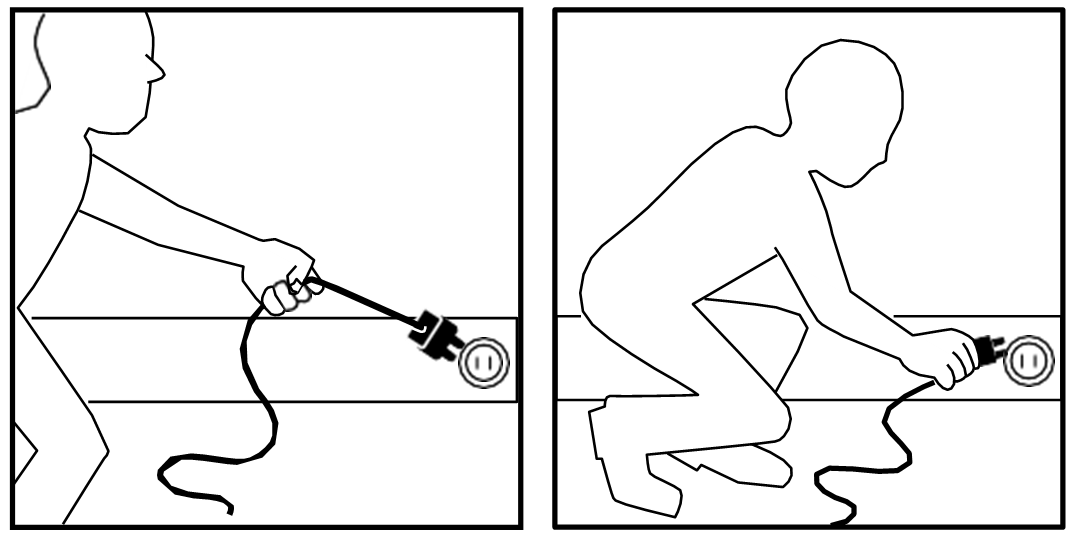
Do not unplug by pulling cord. Always grip the whole plug. - USE extension cords with appropriate power wattage ratings only to temporarily supply power to an area that does not have a power outlet.
- INSTALL permanent wiring if extension cords are constantly in use.
- KEEP power cords away from heat, water and oil. They can damage the insulation and cause a shock.
- DO NOT bypass the on/off switch and operate the tools by connecting and disconnecting the power cord.
- DO NOT USE electric tools in wet conditions or damp locations.
- DO NOT CLEAN electric equipment and tools with flammable or toxic solvents.
- DO NOT CARRY electrical tools by the power cord.
- DO NOT TIE power cords in knots. Knots can cause short circuits and shocks. Loop the cords or use a twist lock plug.
- DO NOT PLUG several power cords into one outlet.
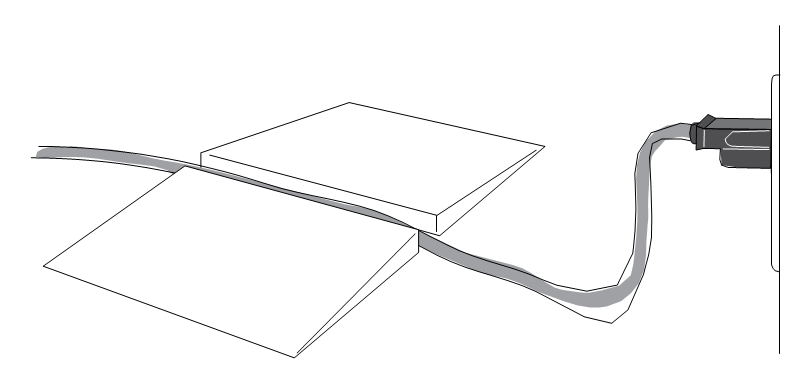
- DO NOT DISCONNECT power supply by pulling or jerking cord from the outlet. Pulling the cord causes wear and may cause a shock.
- DO NOT USE extension cords as permanent wiring.
- DO NOT ALLOW carts and trolleys to pass over unprotected power cords. Cords should be put in conduit or protected by placing planks alongside them.
Fire Prevention and Protection
Fires can be caused by:
- ignition of hot oils and greases
- cardboard and paper materials in contact with hot stoves and ovens
- faulty electrical equipment and cords
- wet electrical equipment and appliances
- faulty switches and power outlets
Portable Fire Extinguishers
Portable fire extinguishers are used to put out small fires. The type of extinguisher to be used depends on the type of fire. You should be trained to use the fire extinguishers used in your workplace. You should also know how to manually operate the built-in CO2 system in range hoods/ ducts.
- ASK your supervisor about fire safety procedures in your workplace.
- KNOW types of fire extinguishers and how to use them. Kitchens may need to have several types of extinguishers, including Class K for fires involving oils and fats.
- IN CASE of fire, you must follow fire safety procedures established by your employer, and approved by the local fire department.
- KNOW fire extinguisher and alarm locations.
- KEEP exits and passageways clear at all times.
- DO NOT ACCUMULATE combustible materials such as cardboard boxes and paper bags in the cooking area in hallways or near exits.
- DO NOT USE electrical wires and equipment which are wet.
- DO NOT USE faulty electrical equipment and cords. DO NOT BRING open flame near hot oils and grease.
A helpful hint: A small fire on a stove or broiler from spilt grease accumulation can be put out with salt, baking soda, or a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher.
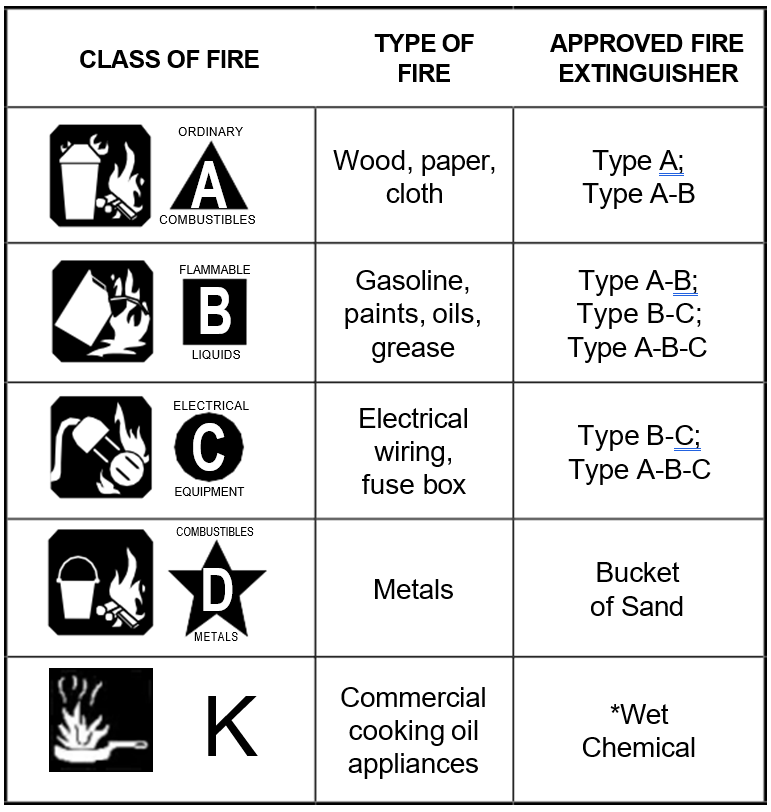
*Class K extinguishers may require specific training, including when they should be used or not used. For example, the extinguishing agents in many Class K extinguishers are electrically conductive and should only be used after electrical power to the kitchen appliance has been shut off.
If a fire occurs:
- SOUND the alarm
- FOLLOW the posted safety procedures that were put in place by your employer and approved by the local fire department, and
- STOP, drop to the ground and roll to smother the flames, if you catch on fire.

