65 Centrifugal Clutches
Learning Objectives
Outcomes: describe the purpose and operation of the centrifugal clutch
Key questions: How does an engine increase or decrease RPM smoothly when starting or under load?
Learning tasks: read course material
Topics: Centrifugal clutch purpose and function
Assessment: online quiz
Estimated time: 0.5 hours
About Centrifugal Clutches
Centrifugal clutches are commonly used in small engine tools such as chainsaws or small motorized vehicles like mopeds. Their function is to link a power provider (engine) to an accelerating load. Operated by the increasing RPM of an engine, they rely on centrifugal force. Occasionally, these clutches may experience slipping, leading to overheating. This is why they are more suitable for smaller machinery rather than automobiles. Centrifugal clutches operate automatically.
The average clutch is a durable device and rarely causes trouble. If your engine is running well but the machinery runs poorly or not at all, you should examine the clutch for slipping. The centrifugal clutch operates the machine when its friction hub presses against a drum. The hub sections are held against a central shaft by springs and will not engage the drum until the engine speed flings them outward. This allows the engine a satisfactory start before taking on the equipment load.
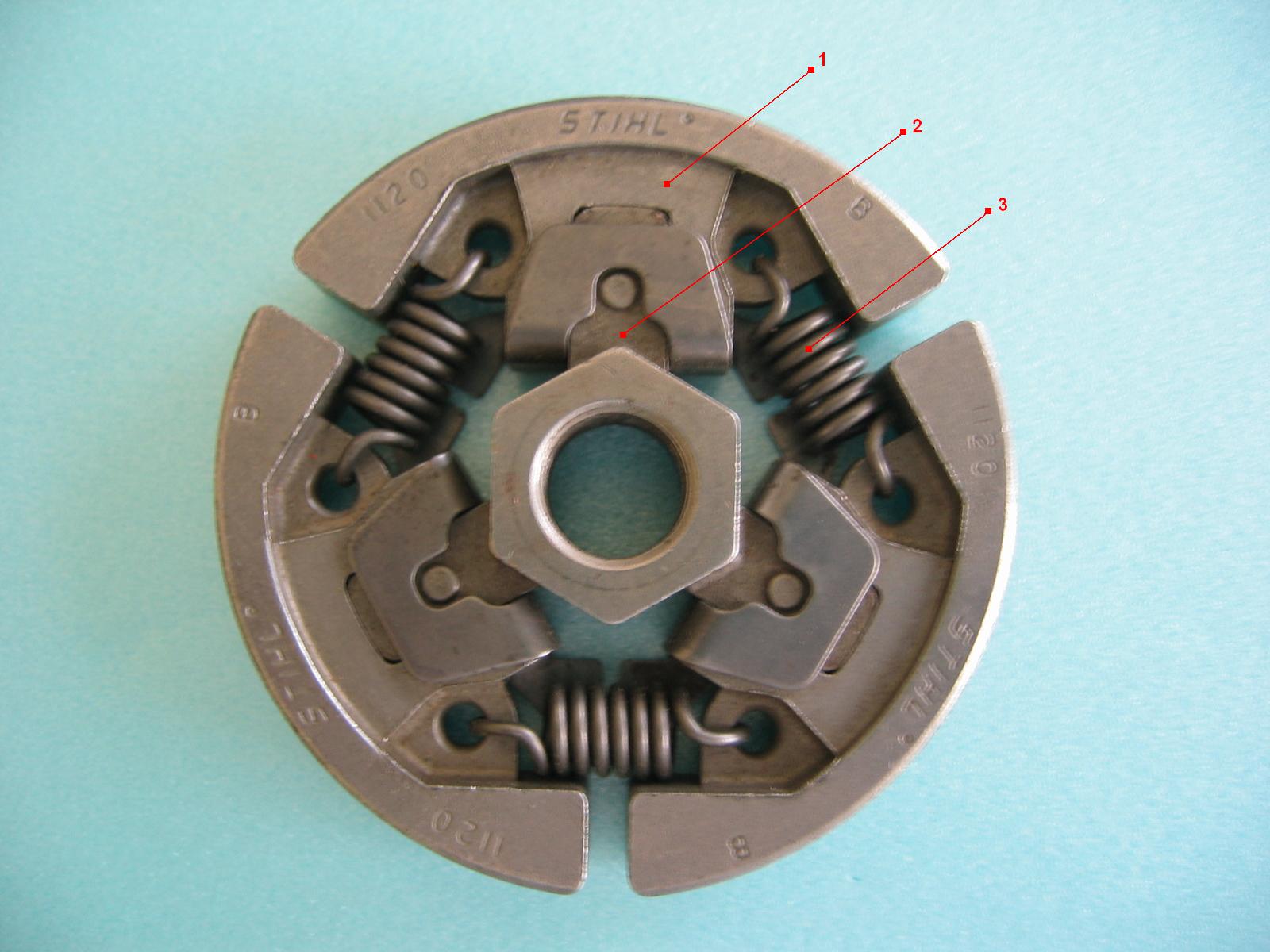
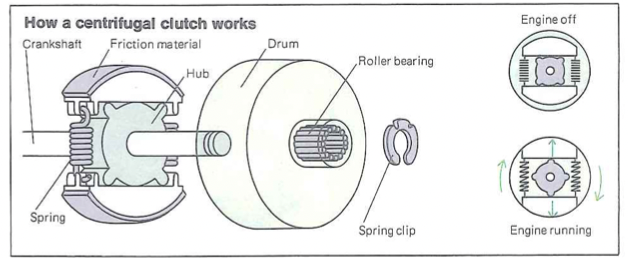
How Centrifugal Clutches Work
Centrifugal clutches work using the centrifugal force. The centrifugal force is a force that occurs when an object is rotating. Within the clutch, this force pushes the clutch shoes (hub) away from the center as it overcomes the force of the springs holding them in place. It is dependent on the speed, or the RPM, that is being delivered to it from the engine. As the engine speed increases, the clutch shoes rotate with the crankshaft. When the engine speeds up and the internal structures rotate, the clutch shoes, attached to springs, move away from the center. That is due to the centrifugal force mentioned earlier. As the clutch shoes move away from the center, they rub against the outer structure (or clutch housing), causing friction.
Removing and Maintaining Centrifugal Clutches
Before dismantling the clutch, remove the spark plug from the engine and rotate the crankshaft to lower the piston. Stuff the upper end of the cylinder with clothesline; it will act as a shock absorber when you knock the clutch loose. Make a large knot at the end of the clothesline to keep the entire length from falling into the engine. Use a feeler gauge to ensure that the clearance between the drum and the friction hub is equal all around. When removed, the clutch invariably has to reverse threading and must be loosened by being turned clockwise, otherwise it would unscrew in normal operation
- If the friction hub is visible, check its clearance from the drum before removing the clutch from the crankshaft. Turn the shaft and watch the hub for irregular movement
- On some engines, the drum will be on the outside of the hub, usually held by a spring clip. Pry off the clip and remove the drum. Spin the hub and check for wobbling
- To remove the hub, pack the cylinder with clothesline then force the hub to turn clockwise swing a hammer and a punch or a dulled old screwdriver
- Examine the inner surfaces of the drum for scoring. Normal friction marks will not snag a fingernail drawn across them. If the nail catches in grooves, replace the drum
- Turn the bearing by hand to detect any roughness in action. Listen for noise. Look for the blue tinge of heat damage. If these symptoms exist, replace the bearing
- If hub movement is irregular or if springs are too weak to keep the hub clearance even when the engine is stopped, replace the hub and springs which are usually sold in sets.
Videos:
Centrifugal clutches explained: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D9d4qXreb8Q (2 min)
How does a centrifugal clutch work?: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p_BbHxCpJiM (3 min)
A centrifugal clutch in normal speed and slow motion: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tSfKmbiqP9g (1 min)
