16 Electronic Controls, Programs, and Sensors
Extra Low Voltage (ELV) systems refer to systems that operate at voltages below 50 volts AC (alternating current) or 120 volts DC (direct current). These systems are typically used for low-power applications such as data communication, security and surveillance, audiovisual systems, and control circuits.
ELV systems are characterized by their low voltage, which reduces the risk of electrical shock and makes them safer to work with compared to higher voltage systems. They are often used in environments where safety is a primary concern, such as hospitals, schools, and public buildings.
 |
 |
ELV systems encompass a wide range of technologies and components, including but not limited to:
Data Communication Systems: This includes Ethernet networks, fiber optic cables, and other communication technologies used for transmitting data within a building or between buildings.

Security and Surveillance Systems: These systems include CCTV cameras, access control systems, and intrusion detection systems, which are used to monitor and secure buildings and premises.
Audiovisual Systems: This includes systems for distributing audio and video signals throughout a building, such as speakers, amplifiers, and video displays.
Control Circuits: These circuits are used to control various building systems, such as lighting, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), as well as industrial processes.

Security and Surveillance
Extra Low Voltage (ELV) systems play a crucial role in modern security and surveillance systems, offering various benefits such as improved safety, flexibility, and efficiency.
CCTV Cameras: ELV systems power and connect CCTV (Closed-Circuit Television) cameras, which are used for monitoring and recording video footage of a building or premises. These cameras typically operate on low-voltage power (usually 12V DC or 24V AC) and transmit video signals over coaxial cables or network cables (such as Ethernet or fiber optic cables) to a central monitoring station or recording device.
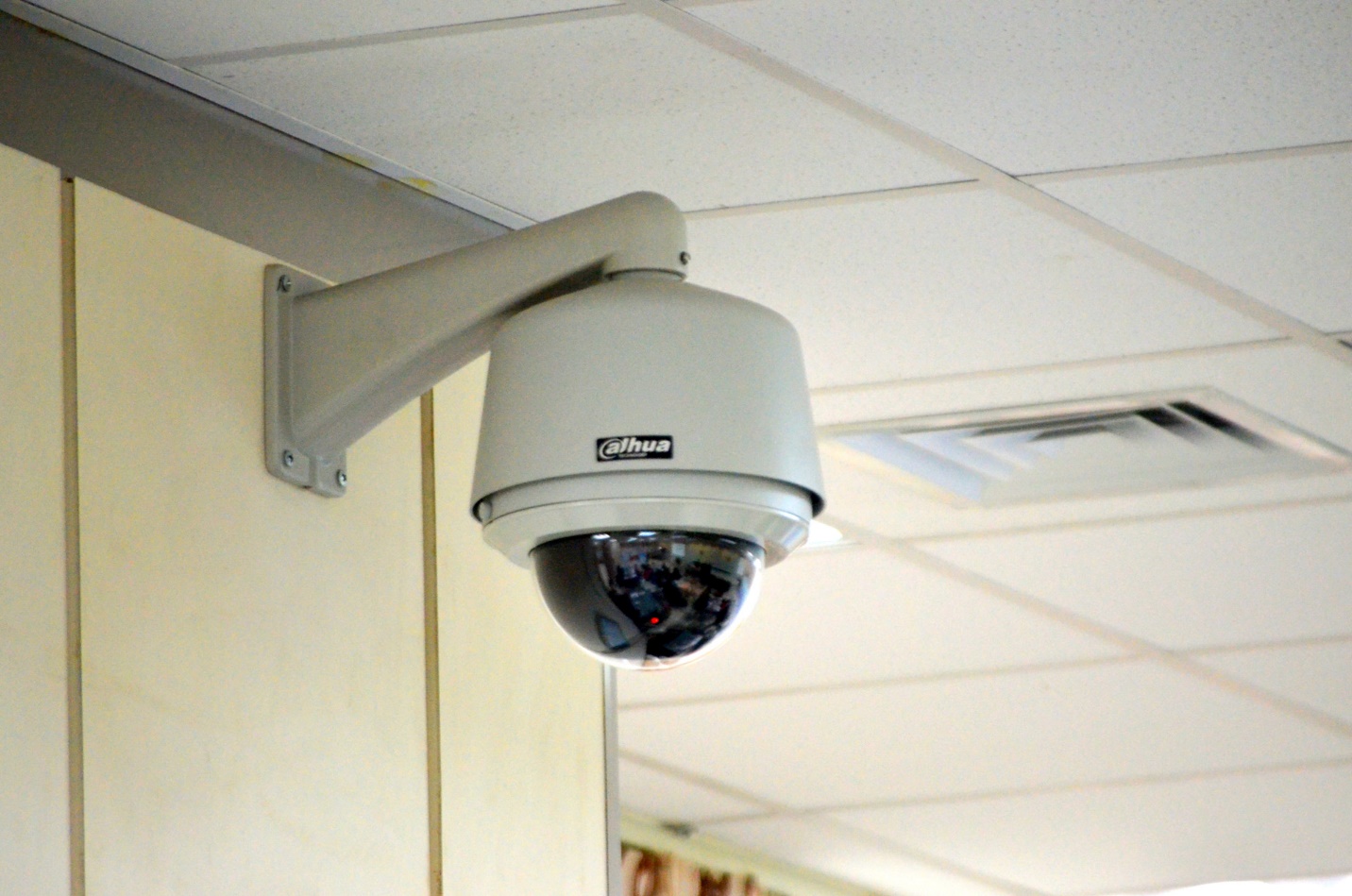

Access Control Systems: ELV systems are utilized to power and connect access control devices such as card readers, keypads, biometric scanners, and electric door locks. These devices often operate on low-voltage power and communicate with a central control panel or software system over data communication networks.
Intrusion Detection Systems: ELV systems power and connect sensors and detectors used in intrusion detection systems, such as motion sensors, door/window contacts, glass break detectors, and vibration sensors. These sensors detect unauthorized entry or movement within a building and trigger alarms or alerts.
Intercom Systems: ELV systems power and connect intercom devices used for two-way audio communication, such as door entry systems, emergency help points, and internal communication systems. These devices often operate on low-voltage power and utilize data communication networks for audio transmission.
Control Circuits
Extra Low Voltage (ELV) systems are integral to controlling building management and HVAC systems, offering a range of functionalities that enhance efficiency, automation, and energy savings.
ELV systems integrate with building management systems which are centralized control systems that monitor and manage various building systems, including HVAC, lighting, security, and fire safety. Building management systems utilize data from sensors and control devices to optimize energy efficiency, comfort, and safety. Sensors such as temperature sensors, humidity sensors, occupancy sensors, and CO2 sensors continuously monitor environmental conditions within the building.
As such, data from sensors and control devices, via an ELV system, interface with an energy management systems (EMS), which is a software applications that analyze energy consumption data and optimize energy usage in buildings. The EMS uses data from sensors and meters to identify energy-saving opportunities, implement energy-saving strategies, and track energy performance over time.
Here’s are some other applications of ELV systems:
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): ELV systems often incorporate PLCs, which are specialized digital computers used to control and automate industrial processes. PLCs in building management systems receive data from sensors, process this data based on programmed logic, and control various building systems accordingly.
Actuators and Control Valves: ELV systems power and control actuators and control valves that regulate HVAC systems, such as motorized dampers, valves, and variable frequency drives (VFDs). These actuators and valves adjust airflow, water flow, and temperature to maintain optimal environmental conditions within the building.
Remote Monitoring and Control: ELV systems enable remote monitoring and control of building management and HVAC systems via computer networks, mobile devices, and web-based applications. This allows building operators to monitor system status, adjust settings, and troubleshoot issues remotely, improving operational efficiency and responsiveness. A general description of how a remote control relay system is discussed next.
Remote Control Relay Systems
A remote control relay system works by using a combination of electronic components to remotely control the operation of electrical devices or circuits. Here’s how it typically functions:
Remote Control Transmitter: The system includes a remote control transmitter, which is a handheld device or controller that sends wireless signals to the relay system. This transmitter may utilize various communication technologies such as radio frequency (RF), infrared (IR), Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi to send control signals to the relay system.
Remote Control Receiver: The relay system features a remote control receiver that is designed to receive signals from the transmitter. The receiver is equipped with a corresponding communication technology that matches the transmitter’s signal transmission method. When the receiver detects a valid control signal from the transmitter, it processes the signal and activates the relay accordingly.
Relay Module: The relay module is the central component of the system responsible for controlling electrical devices or circuits. It typically consists of one or more relays, which are electromagnetic switches that can be remotely controlled to open or close electrical contacts. When the relay receives a signal from the remote control receiver, it activates or deactivates the electrical circuit connected to its contacts.
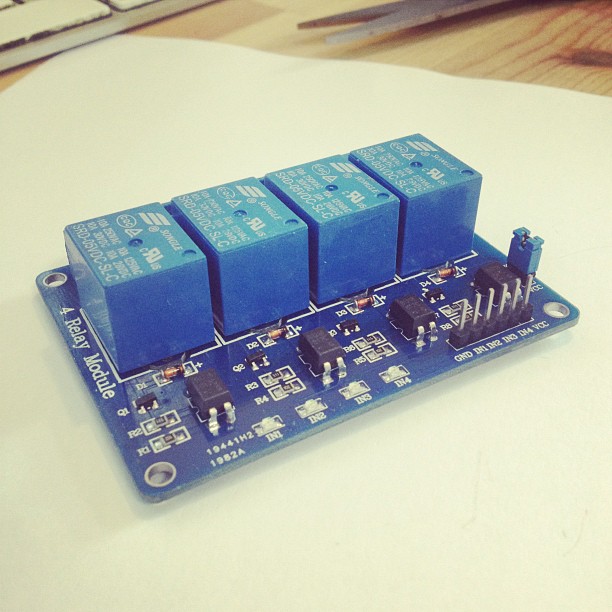
Electrical Load: The electrical load refers to the device or circuit that is controlled by the relay system. This could be anything from lights, fans, motors, heaters, or any other electrical appliance. When the relay is activated by the remote control signal, it completes the circuit and allows electricity to flow to the load, turning it on. When the relay is deactivated, it interrupts the circuit, cutting off power to the load and turning it off.
Power Supply: The relay system requires a power supply to operate. This could be a direct connection to an electrical outlet or a battery-powered system, depending on the specific design and application requirements.
Overall, a remote control relay system enables users to wirelessly control electrical devices or circuits from a distance using a remote control transmitter. It offers convenience, flexibility, and automation capabilities for various applications in industrial control, security systems, and remote monitoring.
